Understanding the Uses of Laparoscopic Trocars
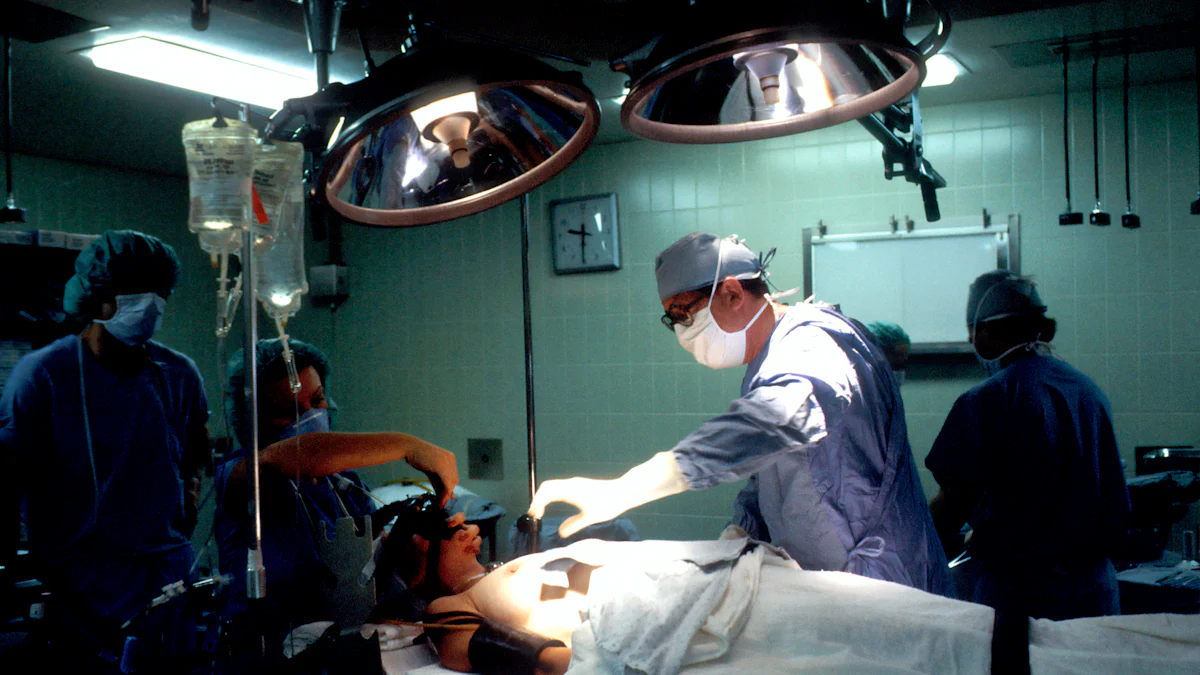
In the realm of surgical innovation, laparoscopic procedures have revolutionized traditional practices. Laparoscopic trocars serve as indispensable tools in these minimally invasive surgeries, facilitating precise access points for instruments and cameras within the abdominal cavity. This blog delves into the significance and multifaceted utility of laparoscopic trocars, shedding light on their pivotal role in modern surgical techniques.
Historical Context of Laparoscopic Trocars
Evolution of Laparoscopic Surgery
In 1911, H.C. Jacobaeus introduced the term 'laparothorakoskopie' and utilized a trocar directly without pneumoperitoneum, marking a significant milestone in surgical history. This innovative approach revolutionized procedures for both thoracic and abdominal surgeries.
Early Techniques and Instruments
The early techniques and instruments used in laparoscopic surgery paved the way for modern advancements. Surgeons like Kurt Semm, in 1966, played a crucial role by introducing an automatic insufflation device, reducing the risks associated with abdominal insufflation.
Introduction of Trocars
Professor Hopkins' discovery of the rigid rod lens system in 1953 was a groundbreaking development that transformed the concept of videoscopic surgery. This introduction laid the foundation for enhanced visualization during laparoscopic procedures.
Advancements in Trocar Design
Technological improvements have continuously enhanced the design and functionality of trocars over time, leading to improved surgical outcomes and patient care.
Technological Improvements
With ongoing technological advancements, laparoscopic trocars have evolved to become more precise and efficient tools in minimally invasive surgeries. These improvements have significantly contributed to the success rates of laparoscopic procedures.
Impact on Surgical Outcomes
The impact of advanced trocar designs on surgical outcomes cannot be overstated. By providing better access points and instrument insertion capabilities, modern trocars have revolutionized the field of laparoscopic surgery.
Technical Details of Laparoscopic Trocars
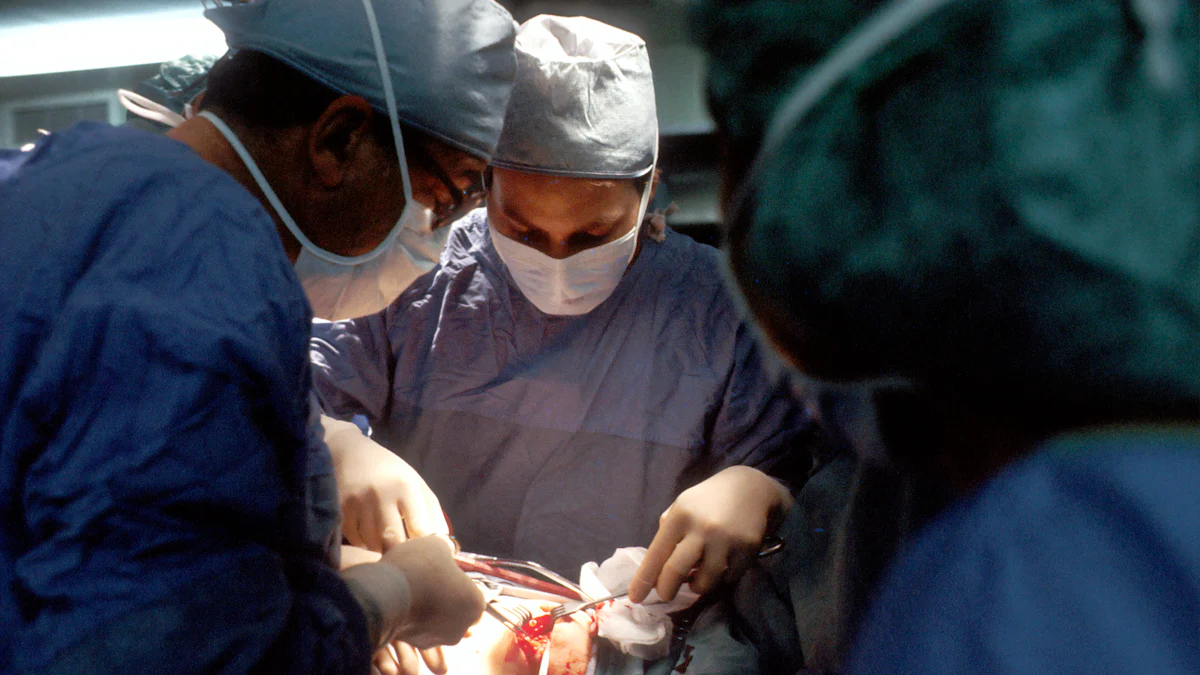
Types of Trocars
Bladed vs. Bladeless Trocars
Bladed Trocars: Feature cutting tips in the shape of a three-edged pyramid or a flat two-edged blade, providing precise entry paths through the abdominal wall.
Bladeless Trocars: Utilize conical tips that are less traumatic to tissues, reducing the risk of herniation or hemorrhage during surgical procedures.
Disposable vs. Reusable Trocars
Disposable Trocars: Offer single-use convenience and sterility, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination and ensuring optimal safety for patients.
Reusable Trocars: Provide cost-effective options for multiple procedures while maintaining quality and efficiency in laparoscopic surgeries.
Components and Features
Cannula
The cannula serves as the outer sleeve of the trocar assembly, creating a pathway for surgical instruments to access the peritoneal cavity with minimal tissue trauma.
Different types of cannulas are available, each designed to accommodate specific surgical needs and ensure precise instrument insertion during procedures.
Obturator
The obturator is the stylet introduced through the cannula, facilitating initial penetration into the abdominal wall with its sharp tip design.
By choosing obturators with appropriate tip configurations, surgeons can optimize tissue penetration while minimizing potential complications during trocar insertion.
Seals and Valves
Valve systems integrated into trocars prevent gas leakage during laparoscopic surgeries, maintaining stable pneumoperitoneum throughout procedures.
Seals within trocar assemblies ensure a secure closure around inserted instruments, enhancing procedural efficiency and reducing the risk of gas leaks or contamination.
Procedural Steps Involving Trocars
Preoperative Preparation
Patient Positioning
Position the patient on the operating table according to the specific surgical requirements.
Ensure proper alignment and support to maintain a stable and comfortable position throughout the procedure.
Secure any necessary restraints or padding to prevent unintended movements during surgery.
Sterilization and Setup
Prepare the surgical site by thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting the area surrounding the intended trocar insertion points.
Use sterile drapes to create a sterile field, minimizing the risk of contamination during trocar placement.
Arrange all required instruments and equipment in an organized manner to facilitate a smooth transition during the surgical procedure.
Trocar Insertion Techniques
Veress Needle Technique
Make a small incision at the designated entry point for trocar insertion using a scalpel or other appropriate cutting tool.
Introduce the Veress needle through the incision, ensuring proper placement within the abdominal cavity under direct visualization.
Confirm correct positioning of the Veress needle by observing appropriate insufflation of gas into the peritoneal cavity.
Direct Trocar Insertion
Identify the optimal entry site for direct trocar insertion based on preoperative planning and patient anatomy.
Apply controlled pressure while inserting the trocar directly through the abdominal wall, maintaining a steady hand to avoid unnecessary tissue trauma.
Verify successful placement of the trocar by visualizing its secure positioning within the abdominal cavity.
Postoperative Considerations
Trocar Removal
Gently remove each trocar from its respective port, taking care to minimize any potential damage to surrounding tissues or organs.
Apply pressure or sutures as needed to close any skin incisions created during trocar removal, ensuring proper wound healing post-surgery.
Wound Care
Cleanse and dress all trocar insertion sites with appropriate antiseptic solutions to prevent infections and promote healing.
Monitor patients closely for any signs of postoperative complications related to trocar insertion sites, such as infection or delayed wound healing.
Practical Applications of Laparoscopic Trocars
Common Surgical Procedures
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy involves the removal of the gallbladder and is a common procedure performed using laparoscopic trocars. Surgeons create small incisions to access the abdominal cavity, enabling precise removal of the gallbladder with minimal invasiveness.
Appendectomy
Appendectomy, the surgical removal of the appendix, is another routine procedure that benefits from the use of laparoscopic trocars. By inserting specialized instruments through small incisions, surgeons can efficiently remove the inflamed appendix, promoting quicker recovery times for patients.
Specialized Uses
Bariatric Surgery
In bariatric surgery, which focuses on weight loss procedures, laparoscopic trocars play a vital role in creating access points for surgical instruments. These trocars enable surgeons to perform intricate procedures with enhanced precision while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues.
Gynecological Procedures
Gynecological procedures, such as hysterectomies or ovarian cyst removals, often utilize laparoscopic trocars for their minimally invasive approach. By employing these specialized tools, gynecological surgeons can navigate complex anatomical structures with greater ease and accuracy.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Trocars
Advantages
Minimally Invasive Nature: Laparoscopic trocars offer a minimally invasive approach, reducing the need for large incisions and resulting in less postoperative pain for patients.
Reduced Recovery Time: The use of laparoscopic trocars leads to quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgeries, allowing patients to return to their daily activities sooner.
Potential Complications
Trocar Site Hernia: In some cases, the insertion sites of trocars may develop hernias post-surgery. Surgeons must carefully monitor patients for any signs of herniation and provide appropriate treatment if necessary.
Infection Risks: Despite strict sterilization protocols, there is a potential risk of infections associated with trocar insertion sites. Proper wound care and monitoring are essential to prevent and manage any postoperative infections.
Hasson introduced an alternative method of trocar placement. He proposed a blunt mini-laparotomy which permits direct visualization of trocar entrance into the peritoneal cavity. A reusable device of similar design to a standard cannula but attached to an olive-shaped sleeve was developed by Hasson. This sleeve would slide up and down the shaft of the cannula and would form an airtight seal at the fascial opening. In addition, the sharp trocar was replaced by a blunt obturator. This cannula is held in place by the use of stay sutures passed through the fascial edges and attached to the body of the cannula.
Highlighting the pivotal role of laparoscopic trocars in modern surgical practices, their significance cannot be overstated. The continuous evolution and technological advancements in trocar design have significantly enhanced surgical outcomes. Looking ahead, future trends promise even more innovative solutions to further streamline laparoscopic procedures. For a deeper understanding of this essential tool, exploring additional resources will provide valuable insights into the intricate world of laparoscopic trocars.
See Also
Achieving Mastery in Aerial Surveillance Using Drone Thermal Imaging
Maximizing isun Analog FPV Thermal Cameras for Drone Use
Utilizing Drones with Thermal Cameras for Law Enforcement Monitoring
The Evolution of Drone Inspections with FPV Thermal Cameras
Discovering the Advantages of Analog FPV Thermal Cameras for Drones
Contact Us: Ms. Coco Huang
E-mail: sales@iasun.cn
WhatsApp/Wechat: +86 13510421923

